There are numerous available factors that can impact the cost of a rendering. Here are its main types:
1.Complexity of the scene
The higher the complexity of a 3D scene, the much more rendering time it will require; hence fetches a higher price. High polygon counts, more textures, and materials, along with complex lighting setups in a scene will increase the requirement for computational power to render, thus raising costs.
Rendering a simple 3D scene of a cube takes a few minutes, while a detailed cityscape, with very intricate backing buildings, realistic textures, and dynamic lighting might take hours or even days. More complexity means more requirements from more computational power, thus a raise in rendering costs incurred.

2. Resolution and image quality
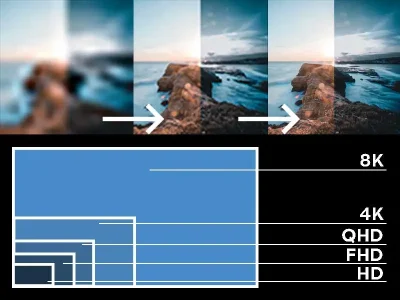
Higher resolutions and high quality settings require more rendering time and computing resources. As an instance, the rendering of a scene at 4K resolution will consume more time and cost more than rendering a similar scene at 1080p.
Imagine you are coloring a huge grid. Each square of the grid is a pixel.
1080p grid: 1920 squares across and 1080 squares down.
4K grid: 3840 squares across and 2160 squares down.
Coloring in the 4K grid will take more time because there are more squares to fill in.
3. Software optimizations
Rendering programs contain special-purpose optimizations designed to speed and enhance the performance of the rendering workflow. These optimizations include:
Parallel Processing: The assignment of tasks is divided into smaller independent tasks that can be processed at the same time, thus shortening rendering time overall.
Caching: Temporary storage of frequently accessed data for the purpose of eliminating redundant calculations and speeding the retrieval process.
Pre-processing: Certain elements and calculations may be prepared in advance so that the actual rendering process can proceed smoothly when the need arises.

4. Hardware
Hardware type and quality place a great influence on rendering performance and speed. Such hardware key factors include:
CPU Cores: The more the cores, the better simultaneous execution of various tasks is done efficiently.
RAM: Larger and faster RAM give more room to house complex scenes and huge data making it faster.
GPU: Great GPU has the capacity to reduce rendering time considerably just by performing efficient processing of graphical computations and complex visual effects.

5.Timeframe for completion
Depending on the type of project, it might be provided with a tighter deadline and thus more resources would be consumed to complete the rendering in the least amount of time. This of course brings an increase in the costs of the rendering service.
Normal Situation: A project has a reasonable timeline, where optimal usage of available resources (like computer processing power and time for rendering) comes into play, and costs remain stable.
Tight Deadline: The same project needs to be finished in such a short time that it would require a more powerful computer, possibly using more expensive rendering services, or hiring additional professionals to work extra hours. Hence, all these additional resources would add up to the overall cost of rendering.

6. Additional services
Apart from rendering, the post-processing and compositing comprise additional value-added services that exponentially increase the total production cost factor. The processes are expensive when it comes to time, effort, and professional prowess since they require editing or merging the generated images as per standards, thus giving way to the final output.

Overall, the price of rendering is different for each type of project because the specific requirements might vary. It is important to consider all of these factors when estimating project costs for rendering.


